Treatments
Our experts cover all sort of conditions.
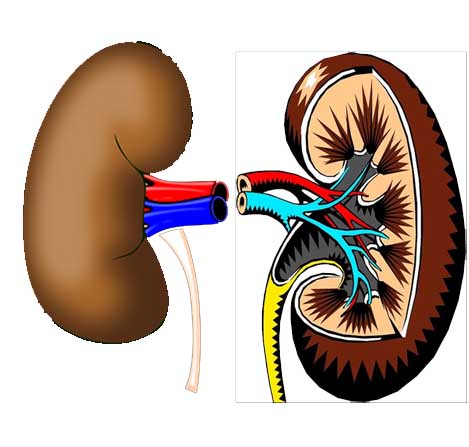
Kidney Infection
A kidney infection is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI). A kidney infection may begin in the tube that carries urine from the body (urethra) or in the bladder. The infection can travel to one or both kidneys. A kidney infection is also called pyelonephritis. A kidney infection needs prompt medical treatment. If not treated properly, an infection can cause lasting damage to the kidneys or the bacteria can spread to the bloodstream and cause a dangerous infection. Kidney infection treatment often includes antibiotics, which might be given in the hospital.
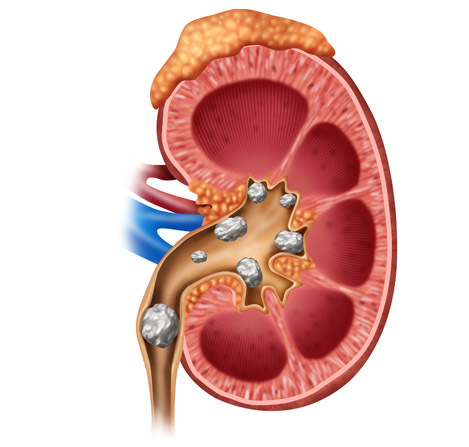
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones form in your kidneys. As stones move into your ureters — the thin tubes that allow urine to pass from your kidneys to your bladder — signs and symptoms can result. Signs and symptoms of kidney stones can include severe pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills and blood in your urine.
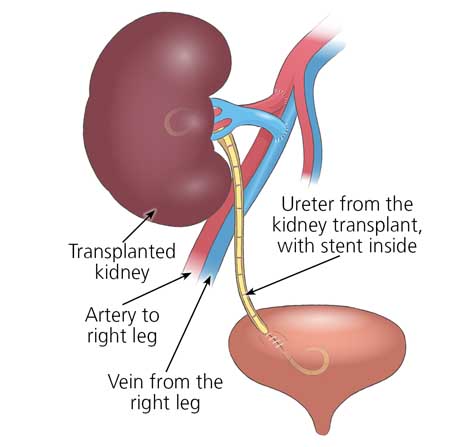
Kidney Transplantation
Kidney or Renal transplant is carried out for patients with advanced kidney failure, i.e., when the kidney function is irreversibly reduced to below 15% of normal. During a kidney transplant, a donor’s kidney is placed is placed into the body of a recipient. The damaged kidneys of the patient are not removed unless required in certain circumstances. Traditionally, kidney transplants were performed with Blood group matched donors. But now with advances in transplant science, even non blood group matched (ABO incompatible) donors can donate their kidneys to a recipient.
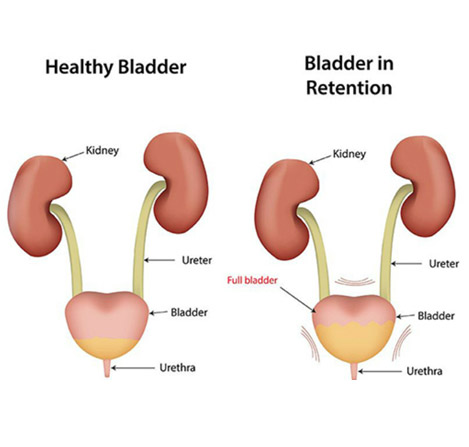
Urinary problems
An infection in any part of the urinary system, the kidneys, bladder or urethra. Urinary tract infections are more common in women. They usually occur in the bladder or urethra, but more serious infections involve the kidney. A bladder infection may cause pelvic pain, increased urge to urinate, pain with urination and blood in the urine. A kidney infection may cause back pain, nausea, vomiting and fever. Common treatment is with antibiotics.
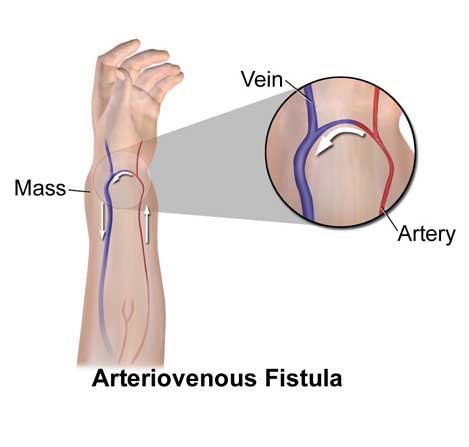
A V Fistula
An arteriovenous (AV) fistula is an irregular connection between an artery and a vein. Blood flow avoids tiny blood vessels (capillaries) and moves directly from an artery into a vein. An arteriovenous (AV) fistula is an irregular connection between an artery and a vein.
Pediatric Nephrology
If your child has kidney or urinary tract disease, bladder problems, kidney stones, or high blood pressure, a pediatric nephrologist has the special skills and experience to treat your child. Pediatric nephrologists treat children from infancy through late adolescence and in some centers up to young adulthood.
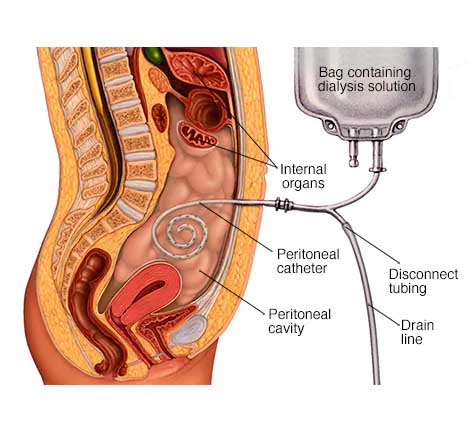
Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis is a treatment for kidney failure that uses the lining of your abdomen, or belly, to filter your blood inside your body. Health care providers call this lining the peritoneum. A few weeks before you start peritoneal dialysis, a surgeon places a soft tube, called a catheter, in your belly.
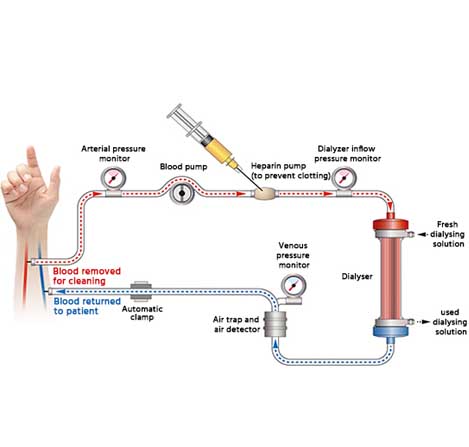
Hem dialysis
When the kidneys stop working, the work of the kidneys to filter blood is carried out by the dialysis process. In the dialysis machine, the blood passes through a filter known as a dialyser, which imitates the kidney and filters out impurities and water from the blood. This process is known as Hemodialysis. She has expertise in planning advanced dialysis therapies for critical patients, such as acute hemodialysis, Slow Low Efficiency Dialysis (SLED) and Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) for critical patients who have very low BP or are unstable in the intensive care unit.
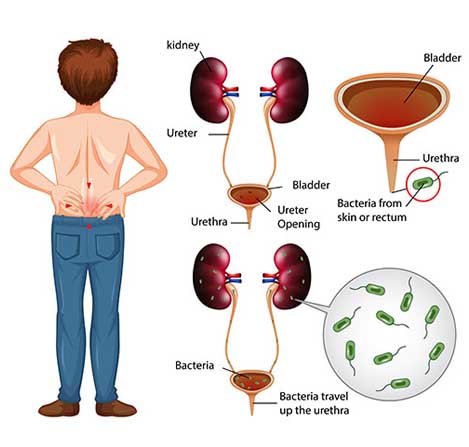
Urinary Tract Infections
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part of the urinary system. The urinary system includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract - the bladder and the urethra. Women are at greater risk of developing a UTI than are men. If an infection is limited to the bladder, it can be painful and annoying. But serious health problems can result if a UTI spreads to the kidneys.
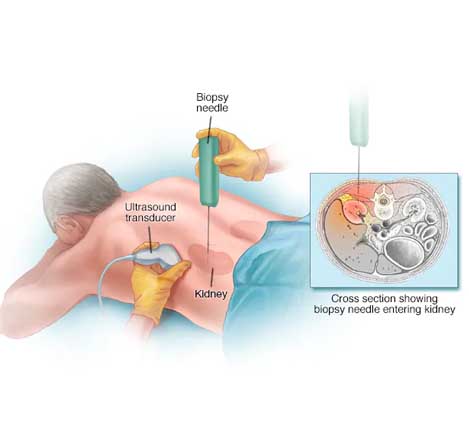
Kidney Biopsy
A kidney biopsy (also called renal biopsy) involves taking one or more tiny samples of the kidney to look at the kidney tissue with a special microscope, for signs of damage or disease.
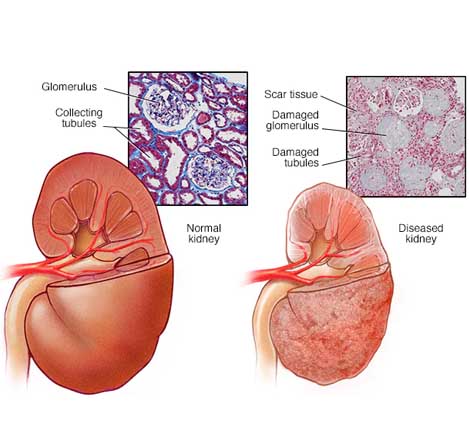
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) means that your kidneys have suffered irreversible damage. Chronic means it is long term and CKD can get worse over time. CKD usually does not have any symptoms until your kidneys are damaged. Blood and Urine tests are used to determine the amount of kidney damage. Blood creatinine level helps to determine the level of damage to the kidneys.